https://arxiv.org/pdf/2108.12184v1.pdf
Abstract
GLOCAL-K(Global-Local Kernel-based matrix)
: 추천시스템에 많이 쓰이는 high-dimensional sparse user-item matrix를 중요한 feature만 뽑은 low-dimensional space로 나타내는 알고리즘
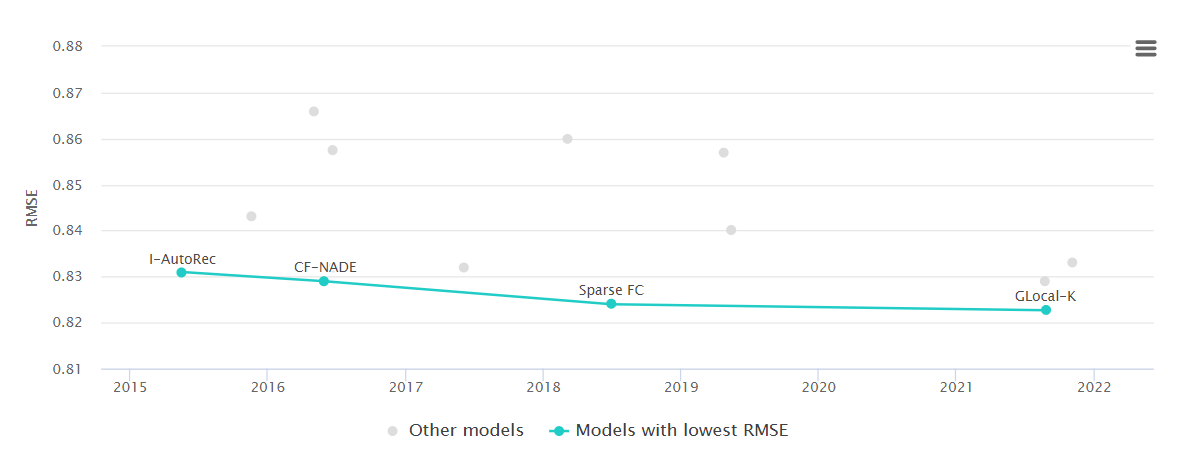
현재까지의 추천시스템 알고리즘에서 가장 좋은 성능을 보임.
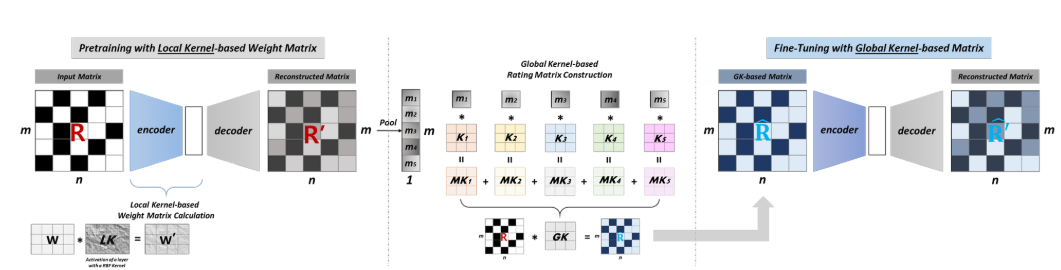
두가지 stage로 이루어짐
stage 1 : Pre-training with Local Kernelised weight matrix (대충 한번 train시키고)
stage 2 : Fine-tuning with Global Kernel based matrix (더 정확하게 tuning하고)
GLOCAL-K
matrix form
m개의 items i∈ 𝐼 = {1, 2, ..., 𝑚}
n개의 users
rating 𝑟𝑖 = (𝑅𝑖1, 𝑅𝑖2, ..., 𝑅𝑖𝑛) ∈ R𝑛
stage 1 : Pre-training with Local Kernel
- Auto-encoder Pre-training
input으로 𝑟𝑖, output으로 𝑟i′을 넣는다.
model
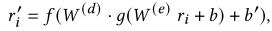
𝑊(𝑑), 𝑊(𝑒) = weight matrices
𝑏, 𝑏′ = bias vectors
𝑓(), 𝑔() = non- linear activation function. (여기선 auto-associative neural network with a single h-dimensional hidden layer을 사용했다고 함.)
- Local kernelised Weight Matrix
아까 model로 구한 𝑊(𝑑), 𝑊(𝑒)를 2d-RBF kernel(local kernelised weight matrix)로 reparameterise함.
RBF kernel
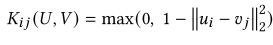
K() = U,V간의 similarity 구하는 RBF kernel function
이 kernel function을 거친 output은 kernel matrix LK라고 부름
def local_kernel(u, v):
dist = tf.norm(u - v, ord=2, axis=2)
hat = tf.maximum(0., 1. - dist**2)
return hat
local kernelised weight matrix
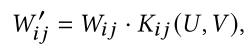
Hadamard-product을 사용해 weight matrix를 reparameterize.
def kernel_layer(x, n_hid=n_hid, n_dim=n_dim, activation=tf.nn.sigmoid, lambda_s=lambda_s, lambda_2=lambda_2, name=''):
with tf.variable_scope(name, reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE):
W = tf.get_variable('W', [x.shape[1], n_hid])
n_in = x.get_shape().as_list()[1]
u = tf.get_variable('u', initializer=tf.random.truncated_normal([n_in, 1, n_dim], 0., 1e-3))
v = tf.get_variable('v', initializer=tf.random.truncated_normal([1, n_hid, n_dim], 0., 1e-3))
b = tf.get_variable('b', [n_hid])
w_hat = local_kernel(u, v)
sparse_reg = tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(lambda_s)
sparse_reg_term = tf.contrib.layers.apply_regularization(sparse_reg, [w_hat])
l2_reg = tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(lambda_2)
l2_reg_term = tf.contrib.layers.apply_regularization(l2_reg, [W])
W_eff = W * w_hat # Local kernelised weight matrix
y = tf.matmul(x, W_eff) + b
y = activation(y)
return y, sparse_reg_term + l2_reg_term
이러한 과정을 통해 weight matrix를 regularising하고 generalisable하게 만들어줌
stage 2 : Fine-tuning with Global Kernel
- Global kernel-based Rating Matrix
item-based average pooling
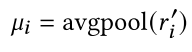
item information을 summarise함.
inner product
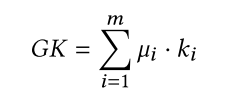
pooling으로 나온 𝜇들을 aggregated 한다.
여기서 각각의 k들은 t*t matrix이다.
def global_kernel(input, gk_size, dot_scale):
avg_pooling = tf.reduce_mean(input, axis=1) # Item (axis=1) based average pooling
avg_pooling = tf.reshape(avg_pooling, [1, -1])
n_kernel = avg_pooling.shape[1].value
conv_kernel = tf.get_variable('conv_kernel', initializer=tf.random.truncated_normal([n_kernel, gk_size**2], stddev=0.1))
gk = tf.matmul(avg_pooling, conv_kernel) * dot_scale # Scaled dot product
gk = tf.reshape(gk, [gk_size, gk_size, 1, 1])
return gk
global kernel-based rating matrix
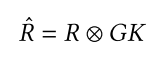
⊗는 convolution operation을 말한다.
def global_conv(input, W):
input = tf.reshape(input, [1, input.shape[0], input.shape[1], 1])
conv2d = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(input, W, strides=[1,1,1,1], padding='SAME'))
return tf.reshape(conv2d, [conv2d.shape[1], conv2d.shape[2]])
- Auto-encoder Fine-tuning
global kernel-based rating matix를 input으로 두고 reconstructed matrix를 output으로 둠
Network
#pre-training
y = R
reg_losses = None
for i in range(n_layers):
y, reg_loss = kernel_layer(y, name=str(i))
reg_losses = reg_loss if reg_losses is None else reg_losses + reg_loss
pred_p, reg_loss = kernel_layer(y, n_u, activation=tf.identity, name='out')
reg_losses = reg_losses + reg_loss
# L2 loss
diff = train_m * (train_r - pred_p)
sqE = tf.nn.l2_loss(diff)
loss_p = sqE + reg_losses
optimizer_p = tf.contrib.opt.ScipyOptimizerInterface(loss_p, options={'disp': True, 'maxiter': iter_p, 'maxcor': 10}, method='L-BFGS-B')#fine-tuning
y = R
reg_losses = None
for i in range(n_layers):
y, _ = kernel_layer(y, name=str(i))
y_dash, _ = kernel_layer(y, n_u, activation=tf.identity, name='out')
gk = global_kernel(y_dash, gk_size, dot_scale) # Global kernel
y_hat = global_conv(train_r, gk) # Global kernel-based rating matrix
for i in range(n_layers):
y_hat, reg_loss = kernel_layer(y_hat, name=str(i))
reg_losses = reg_loss if reg_losses is None else reg_losses + reg_loss
pred_f, reg_loss = kernel_layer(y_hat, n_u, activation=tf.identity, name='out')
reg_losses = reg_losses + reg_loss
# L2 loss
diff = train_m * (train_r - pred_f)
sqE = tf.nn.l2_loss(diff)
loss_f = sqE + reg_losses
optimizer_f = tf.contrib.opt.ScipyOptimizerInterface(loss_f, options={'disp': True, 'maxiter': iter_f, 'maxcor': 10}, method='L-BFGS-B')#train and test loop
best_rmse_ep = 0
best_rmse = float("inf")
time_cumulative = 0
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
for i in range(epoch_p):
tic = time()
optimizer_p.minimize(sess, feed_dict={R: train_r})
pre = sess.run(pred_p, feed_dict={R: train_r})
t = time() - tic
time_cumulative += t
error = (test_m * (np.clip(pre, 1., 5.) - test_r) ** 2).sum() / test_m.sum() # test error
test_rmse = np.sqrt(error)
error_train = (train_m * (np.clip(pre, 1., 5.) - train_r) ** 2).sum() / train_m.sum() # train error
train_rmse = np.sqrt(error_train)
print('.-^-._' * 12)
print('PRE-TRAINING')
print('Epoch:', i+1, 'test rmse:', test_rmse, 'train rmse:', train_rmse)
print('Time:', t, 'seconds')
print('Time cumulative:', time_cumulative, 'seconds')
print('.-^-._' * 12)
for i in range(epoch_f):
tic = time()
optimizer_f.minimize(sess, feed_dict={R: train_r})
pre = sess.run(pred_f, feed_dict={R: train_r})
t = time() - tic
time_cumulative += t
error = (test_m * (np.clip(pre, 1., 5.) - test_r) ** 2).sum() / test_m.sum() # test error
test_rmse = np.sqrt(error)
error_train = (train_m * (np.clip(pre, 1., 5.) - train_r) ** 2).sum() / train_m.sum() # train error
train_rmse = np.sqrt(error_train)
if test_rmse < best_rmse:
best_rmse = test_rmse
best_rmse_ep = i+1
print('.-^-._' * 12)
print('FINE-TUNING')
print('Epoch:', i+1, 'test rmse:', test_rmse, 'train rmse:', train_rmse)
print('Time:', t, 'seconds')
print('Time cumulative:', time_cumulative, 'seconds')
print('.-^-._' * 12)# Final result
print('Epoch:', best_rmse_ep, ' best rmse:', best_rmse)https://github.com/usydnlp/Glocal_K
GitHub - usydnlp/Glocal_K
Contribute to usydnlp/Glocal_K development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
'Data Science > Recommendation' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Autoencoder, 오토인코더란? (0) | 2022.06.27 |
|---|---|
| [Paper review] Session-based recommendations with Recurrent Neural Networks(RNN) (1) | 2022.04.11 |
| Deep Learning Recommendation Model for Personalization and Recommendation Systems 논문정리/코드구현 (0) | 2021.09.13 |
| Factorization Machine 논문정리/코딩구현 (0) | 2021.09.13 |



